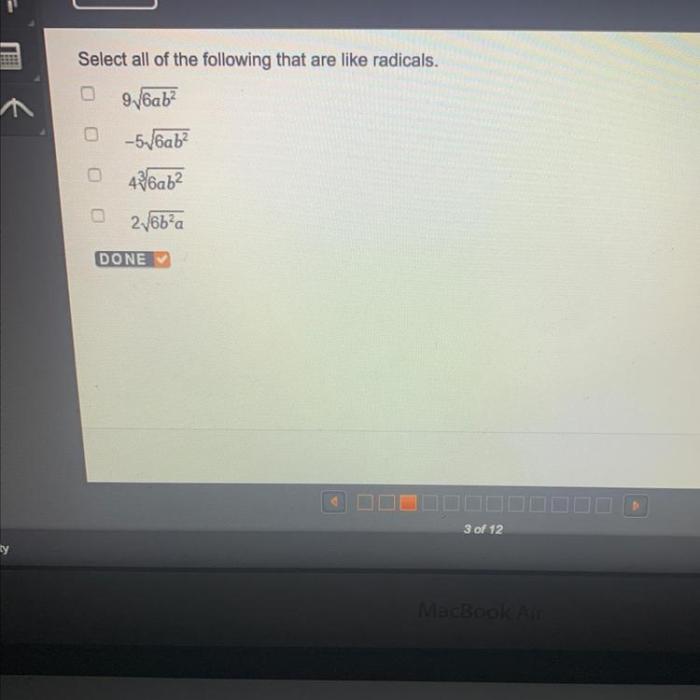
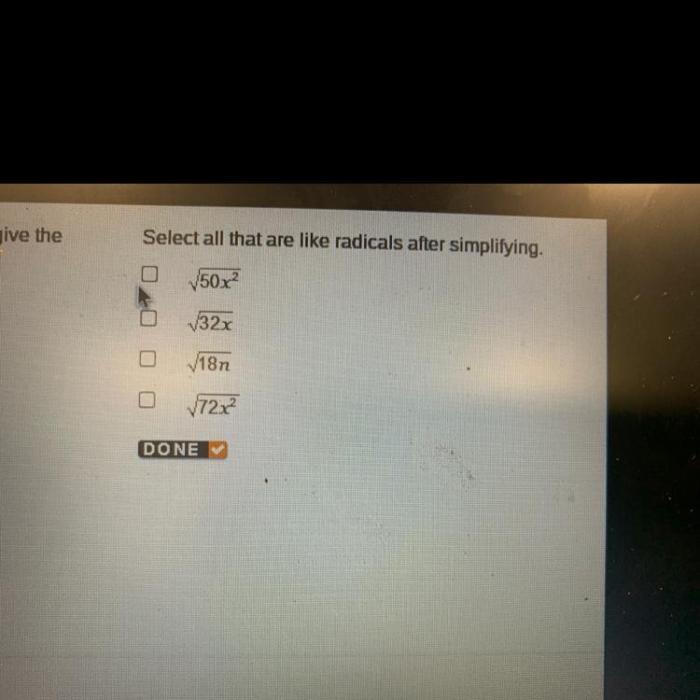
Select all of the following that are like radicals: a journey into the realm of highly reactive chemical species. Radicals, with their unpaired electrons, play a crucial role in various chemical reactions, biological processes, and industrial applications. This guide delves into the fascinating world of radicals, exploring their definitions, properties, significance, and practical uses.
From their historical roots to their involvement in chain reactions and initiation steps, radicals exhibit a unique chemical reactivity. Their role in biological systems, including the production and scavenging of radicals in the body, highlights their potential impact on health and aging.
Furthermore, the practical applications of radicals in fields such as polymer chemistry, the pharmaceutical industry, and environmental remediation showcase their versatility and importance in modern society.
1. Definitions and Origins
Radicals are highly reactive chemical species with unpaired electrons. They are often formed by the homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond, resulting in two radicals with one electron each.
Radicals have been known since the early 19th century, when they were first observed in the context of organic chemistry. The term “radical” was coined by the German chemist Friedrich Wöhler in 1844 to describe the reactive intermediates that he observed in the reactions of organic compounds.
Radicals play an important role in many chemical reactions, including combustion, polymerization, and halogenation. They are also involved in a variety of biological processes, such as respiration and photosynthesis.
Types of Radicals
- Free radicals: Free radicals are radicals that are not attached to any other atoms or molecules. They are highly reactive and can react with a variety of other molecules, including DNA, proteins, and lipids.
- Alkyl radicals: Alkyl radicals are radicals that are derived from alkanes. They are typically formed by the homolytic cleavage of a C-H bond.
- Hydroxyl radicals: Hydroxyl radicals are radicals that are derived from water. They are typically formed by the homolytic cleavage of an O-H bond.
2. Chemical Properties
Radicals are highly reactive chemical species due to their unpaired electrons. They can react with a variety of other molecules, including other radicals, molecules with double bonds, and molecules with lone pairs of electrons.
Radicals play an important role in chain reactions. A chain reaction is a reaction in which the product of one reaction is a reactant in the next reaction. Radicals can initiate chain reactions by reacting with a molecule to form a new radical, which can then react with another molecule to form a new radical, and so on.
Radicals are also involved in initiation steps. An initiation step is a reaction that starts a chain reaction. Radicals can initiate chain reactions by reacting with a molecule to form a new radical, which can then react with another molecule to form a new radical, and so on.
Examples of Radical Reactions
- Halogenation: Halogenation is a reaction in which a halogen atom is added to a molecule. Radicals can initiate halogenation reactions by reacting with a halogen molecule to form a new radical, which can then react with a molecule to add a halogen atom.
- Polymerization: Polymerization is a reaction in which a monomer is added to a growing polymer chain. Radicals can initiate polymerization reactions by reacting with a monomer to form a new radical, which can then react with another monomer to add to the growing polymer chain.
- Combustion: Combustion is a reaction in which a fuel reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light. Radicals play an important role in combustion reactions by reacting with oxygen to form new radicals, which can then react with fuel molecules to produce heat and light.
3. Biological Significance: Select All Of The Following That Are Like Radicals
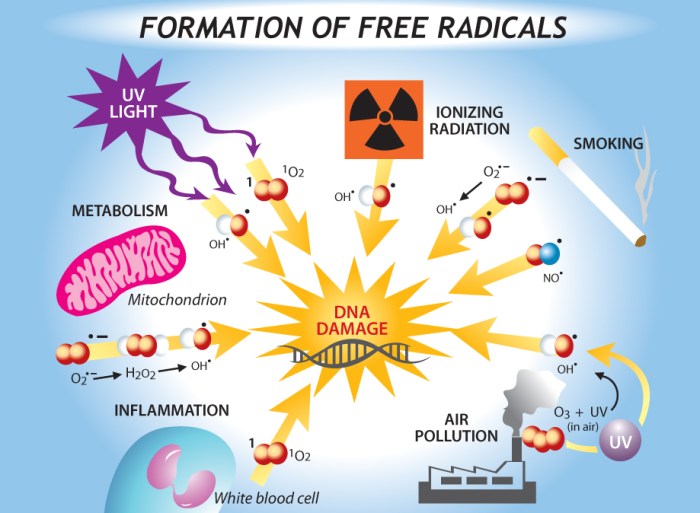
Radicals are involved in a variety of biological processes, including respiration and photosynthesis. They are also produced as a byproduct of metabolism and can damage cells if they are not scavenged.
The body has a number of mechanisms to scavenge radicals, including antioxidants. Antioxidants are molecules that can donate electrons to radicals, neutralizing them and preventing them from damaging cells.
Free radicals have been implicated in a number of diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. However, it is important to note that radicals are also necessary for a number of biological processes, and that the body has a number of mechanisms to scavenge them.
4. Applications of Radicals
Radicals are used in a variety of applications, including polymer chemistry, the pharmaceutical industry, and environmental remediation.
Polymer Chemistry
Radicals are used in the production of a wide variety of polymers, including polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene. These polymers are used in a variety of applications, including packaging, construction, and automotive parts.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Radicals are used in the production of a number of pharmaceuticals, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and anti-cancer drugs. These drugs are used to treat a variety of diseases, including infections, pain, and cancer.
Environmental Remediation, Select all of the following that are like radicals
Radicals are used in the remediation of a variety of environmental pollutants, including chlorinated solvents, pesticides, and dioxins. These pollutants can be harmful to human health and the environment, and radicals can be used to break them down into less harmful compounds.
Key Questions Answered
What are radicals?
Radicals are atoms or molecules with unpaired electrons, making them highly reactive.
What is the role of radicals in biological systems?
Radicals play a role in various biological processes, including metabolism, immune response, and aging.
What are the practical applications of radicals?
Radicals are used in a wide range of applications, such as polymer production, drug development, and environmental cleanup.
