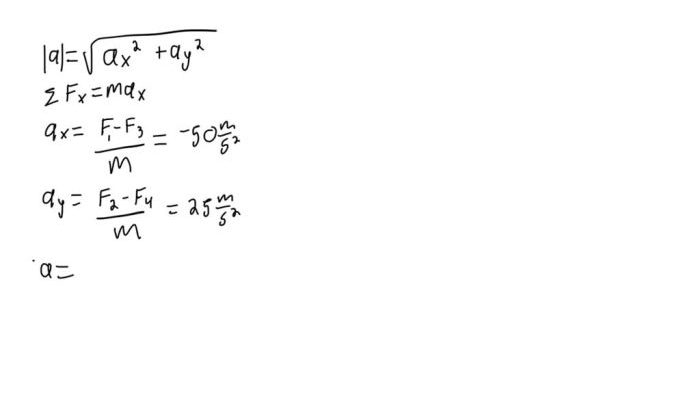A skater increases her speed uniformly, embarking on a journey that unveils the fundamental principles of kinematics. As she glides across the ice, her motion becomes a testament to the intricate relationship between speed, distance, and time, offering a captivating exploration into the realm of uniform motion.
Uniform motion, characterized by constant speed, provides a unique opportunity to delve into the kinematics of motion. This concept serves as the cornerstone of our understanding of how objects move and interact with their surroundings, making it an essential aspect of physics and engineering.
Kinematics of Uniform Motion

Uniform speed refers to the constant rate of motion of an object. In this scenario, a skater increases her speed uniformly, which means her rate of change in speed is constant.
Relationship between Speed, Distance, and Time: A Skater Increases Her Speed Uniformly

The relationship between speed, distance, and time is expressed by the equation: $$v = \fracdt$$ where: – $v$ is speed – $d$ is distance – $t$ is time
Acceleration and Uniform Motion, A skater increases her speed uniformly
Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity. In uniform motion, the velocity is constant, which means the acceleration is zero. This implies that the skater’s speed is not changing over time.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios

Uniform motion is relevant to the skater’s situation as it describes the constant rate at which she increases her speed. Other real-world applications of uniform motion include:
- Cars traveling at a constant speed on a highway
- A ball rolling down a ramp with constant velocity
Advanced Concepts

Instantaneous Velocity
Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object at a specific instant in time. In uniform motion, the instantaneous velocity is equal to the average velocity over any time interval.
Query Resolution
What is uniform motion?
Uniform motion occurs when an object travels at a constant speed in a straight line.
How is speed related to distance and time in uniform motion?
Speed is directly proportional to distance and inversely proportional to time, as expressed by the equation: speed = distance / time.
What is the significance of acceleration in uniform motion?
Acceleration is zero in uniform motion, indicating that the object’s speed is not changing.
Can uniform motion be observed in real-world scenarios?
Yes, uniform motion is commonly observed in various situations, such as a car traveling at a constant speed on a highway or a ball rolling down a smooth incline.