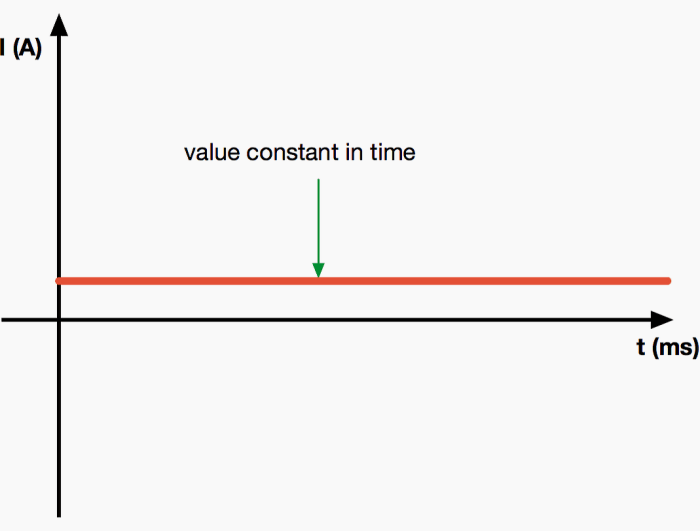
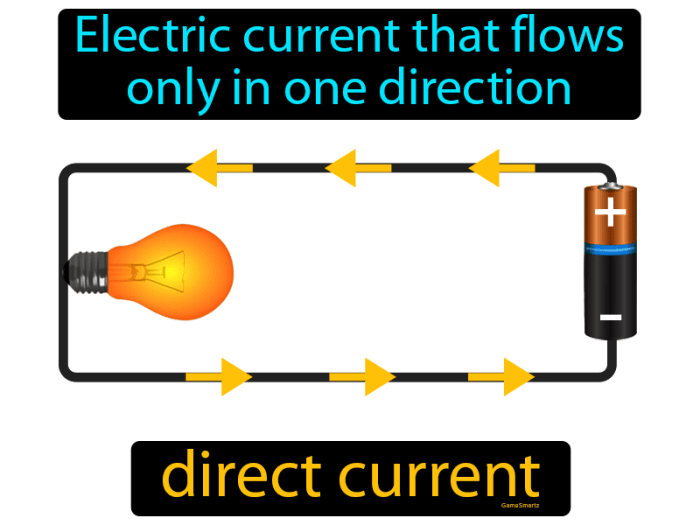
A psu converts alternating current to what – A PSU converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), which is essential for powering electronic devices. AC is the type of electricity that flows through household outlets, while DC is the type of electricity used by most electronic devices.
The conversion process involves several steps and components, including transformers, rectifiers, and filters.
Transformers step up or step down the voltage of the AC current to the desired level. Rectifiers convert the AC current to DC current. Filters smooth out the DC current to remove any remaining AC ripple.
PSU Components and Function: A Psu Converts Alternating Current To What
A Power Supply Unit (PSU) is a critical component of any computer system, responsible for converting alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet into direct current (DC) that powers the system’s various components. The primary components of a PSU include:
- Transformer:Steps up or down the voltage of the AC input.
- Rectifier:Converts the AC input into a pulsating DC output.
- Filter:Smooths out the pulsating DC output into a relatively constant DC voltage.
- Voltage regulator:Maintains a stable output voltage despite variations in the input voltage or load.
These components work together to ensure that the computer system receives a clean and stable supply of DC power.
AC-to-DC Conversion Process, A psu converts alternating current to what
The conversion of AC to DC in a PSU involves several steps:
- Transformer:The transformer steps up or down the voltage of the AC input to a level suitable for the system’s components.
- Rectifier:The rectifier converts the AC input into a pulsating DC output. This is achieved using diodes, which allow current to flow in only one direction.
- Filter:The filter, typically consisting of capacitors and inductors, smooths out the pulsating DC output into a relatively constant DC voltage.
- Voltage regulator:The voltage regulator maintains a stable output voltage despite variations in the input voltage or load. This is achieved using feedback circuits that adjust the output voltage as needed.
PSU Output Types
PSUs provide different types of DC output voltages to power various components within a computer system. Common output voltages include:
- +3.3V:Powers the CPU, RAM, and other low-power components.
- +5V:Powers older peripherals and devices.
- +12V:Powers high-power components such as the CPU, graphics card, and storage devices.
- -12V:Used for legacy devices and some older peripherals.
The output voltage of a PSU is determined by the design of the transformer and the voltage regulators used.
PSU Efficiency and Regulation
PSU efficiency measures the amount of power delivered to the system relative to the power consumed from the wall outlet. Higher efficiency means less power is wasted as heat. PSU efficiency is typically rated using the 80 Plus standard, with levels ranging from 80 Plus to 80 Plus Titanium.PSU
regulation refers to the ability of the PSU to maintain a stable output voltage under varying load conditions. Good voltage regulation is essential for ensuring the stability and reliability of the computer system.
PSU Form Factors and Standards
PSUs come in different form factors to fit various computer cases. Common form factors include:
- ATX:The most common form factor for desktop computers.
- SFX:A smaller form factor designed for compact systems.
- EPS:A high-power form factor used in server and workstation systems.
PSU standards, such as ATX and EPS, define the physical dimensions, mounting points, and electrical specifications of the PSU. Adhering to these standards ensures compatibility with different computer systems.
PSU Selection and Installation
When selecting a PSU, it is important to consider the power requirements of the system’s components. The PSU should provide sufficient wattage to handle the peak power consumption of the system.Installing a PSU involves mounting it in the computer case and connecting it to the motherboard and other components.
Proper installation is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of the system.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between AC and DC current?
AC current flows in one direction and then reverses direction, while DC current flows in only one direction.
Why do electronic devices use DC current?
Most electronic devices use DC current because it is easier to regulate and use than AC current.
What is the efficiency of a PSU?
The efficiency of a PSU is a measure of how much power it converts from AC to DC. A higher efficiency means that less power is lost as heat.